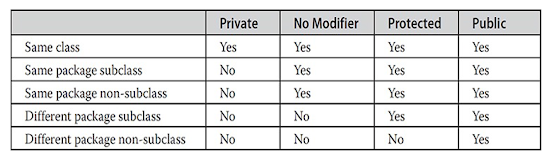
Data Types, Variables and Arrays
Java defines 8 primitive(simle) types of data: byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean. Byte - the smallest integer type. This is a signed 8-bit type that has a range from -128 to 127. Short - is a signed 16-bit type. It has range from -32,768 to 32767. Int - is a signed 32-bit type that has a range from -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647. Long - is a signed 64-bit type. Float - specifies single-precision value that uses 32 bits of storage. Double - uses 64 bits of storage. Char - is 16-bit type. The range of a char 0 to 65,536. There are no negative chars. Boolean - has two possible values true or false. Integer Literals. An integer literal can always be assigned to a long variable. You do this by appending an upper- or lowercase L to the literal. For example, 0x7fffffffL or 12345L. You can also specify integer literals using binary. To do so, prefix the value with 0b or 0B . int x = 0b1010; Octal values are denoted in Java by leading...